Core Vocabulary Metadata
- Publisher
- DG JRC
- Model Version
- 1.5.3
- Status
- Under development
- Doc Version
- 23-Nov-2017
CISE Support Team.
Location CISE Core Vocabulary Specification
Table of Contents
| Model Element | Type |
|---|---|
| CloudCoverType | Enumeration |
| Geometry | Class |
| Location | Class |
| LocationQualitativeAccuracyType | Enumeration |
| LocationZoneType | Enumeration |
| MeteoOceanographicCondition | Class |
| MetocType | Enumeration |
| NamedLocation | Class |
| OperationalPurposeType | Enumeration |
| PortFacilityLocation | Class |
| PortLocation | Class |
| SeaConditionType | Enumeration |
| TidesType | Enumeration |
| WeatherConditionType | Enumeration |
UML Conceptual Model
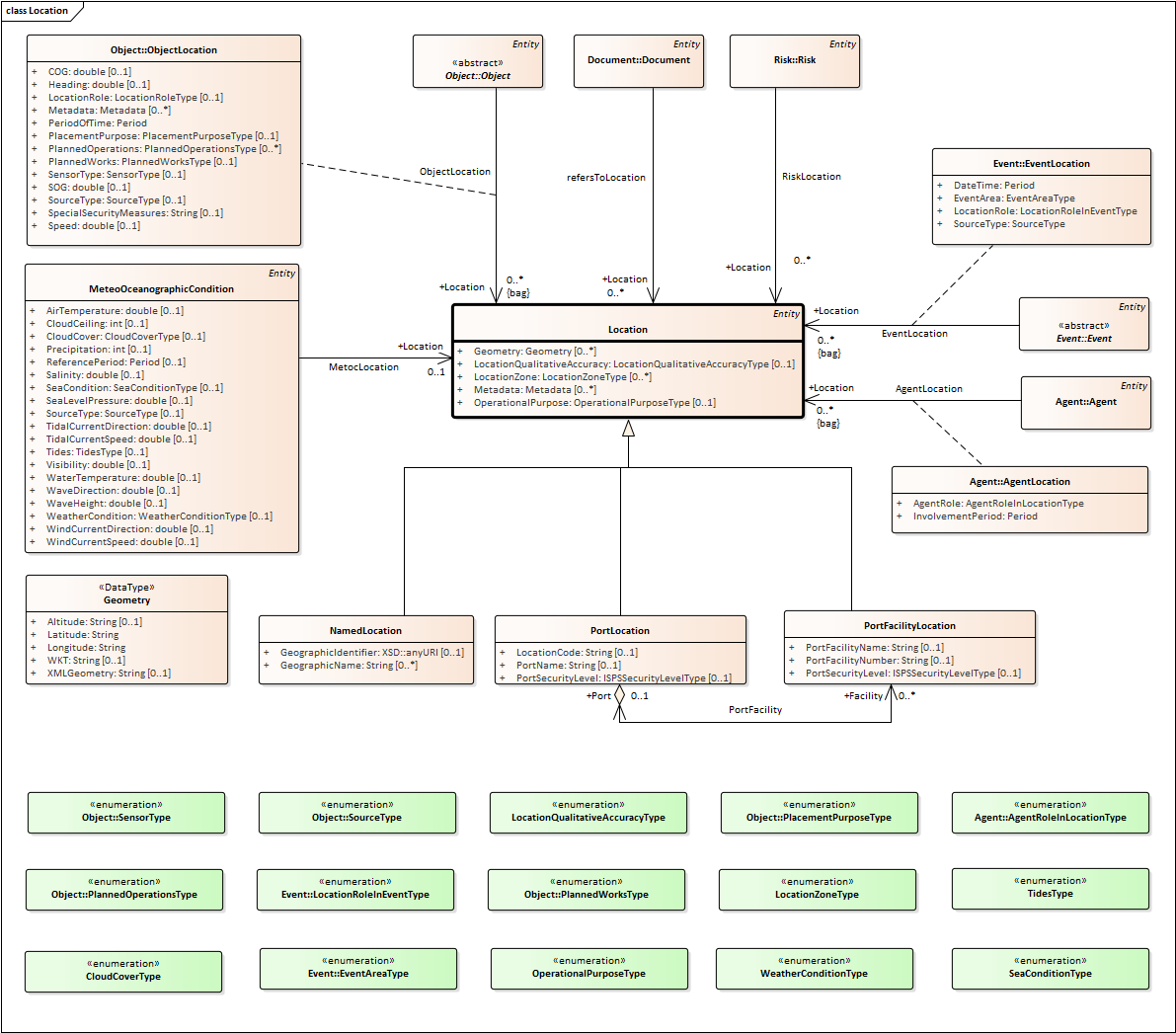
Elements defined in the Core Vocabulary
Location Class, subclass of Entity
Locations can be described in three principal ways: by using a place name, geometry or an address. The specific context will determine which method of describing a location is most appropriate. ISO 19112 defines a location as "an identifiable geographic place". With this in mind, "Eiffel Tower", "Madrid" and "California" are all locations and this is a common way of representing locations in public sector data, i.e. simply by using a recognized name. Such identifiers are common although they can be highly ambiguous as many places share the same or similar names.
In addition to a simple (string) label or name for a Location, the identifier property allows defining a Location by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), such as a GeoNames or DBpedia URI.
No cardinality constraints are placed on any property of the Location class so as to maximize flexibility.
Attributes for Location
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Geometry | A Geometry Object which represents a Georeference |
|
| LocationQualitativeAccuracy | LocationQualitativeAccuracyType | Describes the qualitative accuracy of location: high/medium/low |
High |
| LocationZone | LocationZoneType | Provides the types of location. Enumerated |
High Seas |
| Metadata | Metadata | Provides a placeholder for Metadata |
|
| OperationalPurpose | OperationalPurposeType | Provides the types of operational purpose. Enumerated |
Search area |
MeteoOceanographicCondition Class, subclass of Entity
This class allows the description of the meteorological oceanographic condition of a given Location.
Attributes for MeteoOceanographicCondition
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| AirTemperature | double | Air temperature is a measure of how hot or cold the air is. It is the most commonly measured weather parameter. |
|
| CloudCeiling | int | Ceiling is a measurement of the cloud base height relative to the ground (in meters). |
2000(m) |
| CloudCover | CloudCoverType | Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds when observed from a particular location. |
4 (sky half cloudy) |
| Precipitation | int |
|
|
| ReferencePeriod | Period | Period of reference |
|
| Salinity | double | Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of the sea (in g per Kg of water). |
5 (g/Kg) |
| SeaCondition | SeaConditionType | In oceanography, a sea state is the general condition of the free surface on a large body of water—with respect to wind waves and swell—at a certain location and moment. |
04 (moderate) |
| SeaLevelPressure | double | Atmospheric pressure at sea level (in HPa). |
100.15 (HPa) |
| SourceType | SourceType | Indicate if the oceanographic condition was observed or estimated. Enumerated. |
Observed |
| TidalCurrentDirection | double | Indicates current direction in degrees andknots. The direction always indicates the direction in which the current is flowing |
180 |
| TidalCurrentSpeed | double | Indicates current speed in tenths of knots. |
0.3 |
| Tides | TidesType | Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of gravitational forces exerted by the Moon, Sun, and rotation of the Earth. |
low (low tides) |
| Visibility | double | Visibility should be indicated in nautical miles. |
10 |
| WaterTemperature | double | Water temperature. |
|
| WaveDirection | double | Idicates wave direction in degrees. |
180 |
| WaveHeight | double | Indicates the wave height in metres. |
2 |
| WeatherCondition | WeatherConditionType | Type of weather condition. Enumerated. |
HUM |
| WindCurrentDirection | double | Indicates wind direction in degrees. The direction always indicates from where the wind is blowing. |
270 |
| WindCurrentSpeed | double | Indicates wind speed in m/sec. |
10 |
Association Roles for MeteoOceanographicCondition
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Location | Location in which the METOC were measured. |
0..1 |
Attributes for NamedLocation
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| GeographicIdentifier | XSD::anyURI | A URI that identifies the location. GeoNames.org provides stable, widely recognized identifiers for more than 10 million geographical names that can be used as links to further information. For example, http://sws.geonames.org/593116/ identifies the Lithuanian capital Vilnius. Unfortunately these URIs cannot easily be automatically deduced since the URI scheme uses simple numeric codes. Finding a GeoNames identifier for a Location is almost always a manual process. Where such identifiers are known or can be found, however, it is recommended that they be used. The use of a URIs has added advantages: 1.it can be used by automated systems to look up additional data (linked data); 2. a triple store may store only one copy of the URI, whereas if a string is used, a copy of that string is always stored for each and every person in the database. Thus, in large data sets, the saving on memory capacity and the improvement in transmission efficiency can be substantial. |
http://sws.geonames.org/593116/ |
| GeographicName | String | String A geographic name is a proper noun applied to a spatial object. The following are all valid geographic names for the Greek capital: • Ana (the Greek endonym written in the Greek script) • Athina (the standard Romanisation of the endonym) • Athens (the English language exonym) The country codes defined in ISO 3166 may be used as geographic names and these are generally preferred over either the long form or short form of a country’s name (as they are less error prone). The Publications Office of the European Union recommends the use of ISO 3166-1 codes for countries in all cases except two: • use ‘UK’ in preference to the ISO 3166 code GB for the United Kingdom; • use ‘EL’ in preference to the ISO 3166 code GR for Greece. Where a country has changed its name or no longer exists (such as Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia etc.) use the ISO 3166-3 code [ISO 3166-3]. |
Athens |
| Geometry | Geometry | A Geometry Object which represents a Georeference |
|
| LocationQualitativeAccuracy | LocationQualitativeAccuracyType | Describes the qualitative accuracy of location: high/medium/low |
High |
| LocationZone | LocationZoneType | Provides the types of location. Enumerated |
High Seas |
| Metadata | Metadata | Provides a placeholder for Metadata |
|
| OperationalPurpose | OperationalPurposeType | Provides the types of operational purpose. Enumerated |
Search area |
PortFacilityLocation Class, subclass of Location
Location of one of the facilities contained in a port.
Attributes for PortFacilityLocation
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Geometry | A Geometry Object which represents a Georeference |
|
| LocationQualitativeAccuracy | LocationQualitativeAccuracyType | Describes the qualitative accuracy of location: high/medium/low |
High |
| LocationZone | LocationZoneType | Provides the types of location. Enumerated |
High Seas |
| Metadata | Metadata | Provides a placeholder for Metadata |
|
| OperationalPurpose | OperationalPurposeType | Provides the types of operational purpose. Enumerated |
Search area |
| PortFacilityName | String |
|
|
| PortFacilityNumber | String | Port facility identified by its IMO port facility number. Port facility number is used identify each port facility within each port. Where the whole port is being classified as a single port facility, this number is 0000. The port facility number is not duplicated inside one port but the same number can be reused in different ports. When used in connection with the port code forms an unique identification for each port facility. |
Port facility assigned with number 0000: 0000 |
| PortSecurityLevel | ISPSSecurityLevelType |
|
|
Association Roles for PortFacilityLocation
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Port | PortLocation | 0..1 |
Attributes for PortLocation
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Geometry | A Geometry Object which represents a Georeference |
|
| LocationCode | String | A location is defined as any named geographical place, recognized by a competent national body, either with permanent facilities used for goods movement associated with trade, and used for these purposes, or proposed by the government concerned or by a competent national or international organization for inclusion in the UN/LOCODE. A port is any location with permanent facilities at which vessels can load or discharge cargo moving in maritime traffic. An anchoring area is any location official recommended for anchoring. There are areas dedicated for different type of vessels or general. Such areas are announced in notifications or in sea charts. A code is data transformation or data representation in different forms according to pre-establish rules. (Definition adapted from ISO 5127-1:1983) A code element is result of applying a code to an element in a set of elements to be coded. In UN/LOCODE, one code element represents the name of a port, or a location, i.e. anchoring area, and in addition possible subsidiary location, i.e. an ISPS-area or -terminal. (Definition adapted from ISO 2382-4/1987) A five-character code element is provided for each location included UN/LOCODE and consists of: a) two letters identifying the country, according to the ISO 3166 two-letter Code for the representation of names of countries, and UN/ECE/FAL recommendation No. 3, and b) three characters identifying the location within the country. e.g. A vessel call for Norway, Oslo in the five-character code elements is: “NOOSL” the official Locode list of SSN is obtained from the UNECE (http://www.unece.org/), |
NOOSL |
| LocationQualitativeAccuracy | LocationQualitativeAccuracyType | Describes the qualitative accuracy of location: high/medium/low |
High |
| LocationZone | LocationZoneType | Provides the types of location. Enumerated |
High Seas |
| Metadata | Metadata | Provides a placeholder for Metadata |
|
| OperationalPurpose | OperationalPurposeType | Provides the types of operational purpose. Enumerated |
Search area |
| PortName | String |
|
|
| PortSecurityLevel | ISPSSecurityLevelType | Enumerated. Port's security level according to ISPS standard. |
Port has been assigned the ISPS Security level 2: 02 |
Association Roles for PortLocation
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Facility | PortFacilityLocation | 0..* |
Attributes for Geometry
| UML Name | Data type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude | String | Geographic Altitude, expressed using the WGS84 reference. |
37° 59' 0" N |
| Latitude | String | Geographic Latitude, expressed using the WGS84 reference. |
37° 59' 0" N |
| Longitude | String | Geographic Longitude, expressed using the WGS84 reference. |
23° 44' 0" E |
| WKT | String | Well-known text (WKT) is a text markup language for representing vector geometry objects on a map |
POINT (30 10) |
| XMLGeometry | String | Geometry defined by an XML file such as KML |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2"> <Placemark> <name>Simple placemark</name> <description>Attached to the ground. Intelligently places itself at the height of the underlying terrain. </description> <Point> <coordinates>-122.0822035425683,37.42228990140251,0</coordinates> </Point> </Placemark> </kml> |